LalBrew® LoNa™
LalBrew® LoNa™ is the first maltose-negative Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain specifically developed using hybridization for brewing clean low-alcohol and non-alcohol beers (reduced worty flavors, POF-negative and H2S-negative). Advanced classical and non-GMO breeding methods were used to select a strain that does not consume maltose or maltotriose, resulting in very low attenuation. As a S. cerevisiae strain, LalBrew® LoNa™ performs like an ale yeast producing a clean and neutral aroma profile with no phenolic flavors, and significantly reducing aldehydes that cause worty flavors. Additionally, the patented technology from the University of California Davis (USA) ensures that the strain will not produce sulfurous off-flavors, allowing the malt and hop flavors to shine through.
Pasteurization is required when brewing with LalBrew® LoNa™ to avoid fermentation after packaging and ensure beer stability.
Packaging
500g packs
Quick facts
| Strain | Saccharomyces cerevisiae |
|---|---|
| Attenuation | 16-20% |
| Temperature range | 20 - 25°C (68 - 77°F) |
| Flocculation | Medium |
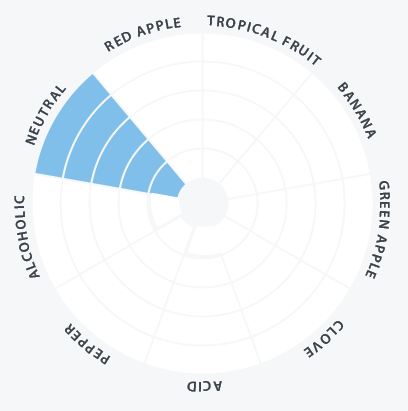
| Aroma | Clean and neutral, no POF or sulfur, wort flavors absent or minimal |
| Pitching rate | 50 - 100g/hL |
Video
More information
To learn more about LalBrew LoNa, visit: www.lallemandbrewing.com/lona
FAQ
- Different acids have different flavor profiles, but all should be food-grade when added.
- LoNa™ is a hybrid Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- LoNa™ is POF- (unlike other maltose negative yeast strains), so the resulting beer is cleaner tasting
- Overall brewers have found beers fermented with LoNa™ to have a refreshing taste and a fruity aroma
- Maltose is relatively less sweet than other sugars (larger sugar molecules are less sweet than smaller ones)
- Remaining maltose is fermentable by other brewing strains, wild yeast, and bacteria. Pasteurization stabilizes the product and prevents microbial activity in the packaged product.
- LoNa can be used for both low-alcohol and non-alcohol beer production with the appropriate recipe design based on the brewer’s desired results
- The definition of low and non-alcohol beer varies by region
- Hybridization centers on classical breeding techniques that involved the mating of two cells
- Genetic engineering involves modern biotechnology techniques (for example homologous recombination, CRISPR)






